This tool uses 1.0 compute credits per hour.
Zone Occupancy Analysis¶
This tool analyzes and summarizes zone occupancy based on the center of the tracked bounding box and user-defined zones to output the following metrics:
- Total Time in Zone: The cumulative time the subject spent in each zone, calculated from the number of frames spent in each zone.
- Zone area: Calculates the areas of the annotated zones within the FOV (Field of view).
- Occupancy Score: Occupation score is a metric derived from the actual zone occupation / expected zone occupation, where the expected zone occupation is the number of frames multiplied by the ratio of the area of the zone and the total area of all zones specified. Occupation scores greater than 1 represent occupation times greater than if the subject spent uniform time in every zone relative to its area.
- Number of Zone Entries and exits: The number of times the subject entered and exited each zone.
- Length of Zone Occupancy Events: Duration of continuous periods of zone occupancy.
- Average Speed in Zone: The average speed of the subject in each zone.
- Instantaneous speed in zone: Calculated from the distance between consecutive keypoint estimates
Parameters¶
| Parameter | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tracking File | True | N/A | Experiment annotations file containing tracking coordinates |
| Zones File | True | N/A | A .CSV file describing zones of interest |
| X Column Name | True | Bounding Box Center X | The name of the x-coordinate column in the experiment annotations file |
| Y Column Name | True | Bounding Box Center Y | The name of the y-coordinate column in the experiment annotations file |
| Time Column Name | True | Frame Timestamp (s) | The name of the time column in the experiment annotations file |
| Unit of Time | False | seconds | The unit of time the data was sampled at |
| Zone Column Name | False | N/A | An optional parameter to specify if the tracking data contains a pre-defined zone identity column |
| Filter Speed | False | True | Flag indicating whether to apply a gaussian filter on the speed estimates |
| Speed Filter Kernel | False | 9 | This determines how many neighboring values are considered in the filtering process. it's usually an odd number (e.g., 3, 5, 7) to have a symmetrical filter |
| Speed Filter Size | False | 1 | The size of the gaussian filter to apply on the speed estimates. this is in units of standard deviation, also known as sigma |
| Pixels Per Cm | False | N/A | Number of pixels in a centimeter |
Details¶
Inputs¶
The tool expects two inputs.
The first input is a tracking.csv file, which is in the IDEAS experiment annotations format. This format requires annotations to be structured in a table with one time-point (i.e., frame) per row, and one or more columns for annotations (e.g., x and y). This tool expects the following collumns:
* Tracking point X: The x coordinate of the center of the bounding box.
* Tracking point Y: The y coordinate of the center of the bounding box.
* Zone Name: The name of the zone if the center of the bounding box is within a zone.
* Frame Timestamp: The time of the frame in either seconds (s) or microseconds (us).
An example of a table that can be used as input to this tool is shown below:
| Global Frame Number | Movie Number | Local Frame Number | Frame Timestamp (s) | Bounding Box Left | Bounding Box Top | Bounding Box Right | Bounding Box Bottom | Bounding Box Center X | Bounding Box Center Y | Confidence | Zone ID | Zone Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0 | 20 | 1.00 | 51.56 | 155.91 | 133.80 | 224.07 | 92.68 | 189.99 | 31.01 | 4272235054 | Rectangular Zone |
| 21 | 0 | 21 | 1.05 | 55.21 | 154.12 | 127.26 | 226.53 | 91.23 | 190.32 | 15.08 | 4272235054 | Rectangular Zone |
| 22 | 0 | 22 | 1.10 |
The second input is a zones.csv file, which is a table with one row per zone and columns for the zone name, and the zone vertices. The vertices can be specified as a list of x and y coordinates for each vertex, or as a center and major and minor axis for an ellipse. This tool expects the following columns:
- Name: The name of the zone.
- Type: The type of the zone, this will be
rectangle,polygon, orellipse. - X # and Y #: A series of columns representing the X coordinates of the zone. If the type is
ellipse, then the columns will beX 0,Y 0, for the centerpoint. If the type isrectangle, then the columns will beX 0,Y 0throughX 3,Y 3. If the type ispolygon, then the columns will beX 0,Y 0throughX n,Y n. - Major & Minor Axis: The major and minor axis diameters of the ellipse.
- Angle: The angle of the major axis of the ellipse.
An example of a table that can be used as input to this tool is shown below:
An example of a table that can be used as input to this tool is shown below:
| ID | Enabled | Name | Description | Type | X 0 | Y 0 | X 1 | Y 1 | X 2 | Y 2 | X 3 | Y 3 | X 4 | Y 4 | Major Axis | Minor Axis | Angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1705078995618 | 1 | Ellipse Zone | ellipse | 179.315 | 422.524 | 94.6154 | 19.6036 | 90 | |||||||||
| 1705079284270 | 1 | Rectangular Zone | rectangle | 78.4144 | 54.4471 | 471.629 | 54.4471 | 471.629 | 295.604 | 78.4144 | 295.604 | ||||||
| 1705079359582 | 1 | Polygon Zone | polygon | 212.18 | 321.923 | 329.802 | 320.769 | 340.18 | 390 | 416.288 | 340.385 | 471.64 | 368.077 | 254.847 | 447.692 |
Valid tracking.csv and the zones.csv file can be generated from an .isxb file using Extract Tracking Data From nVision Movie.
Valid Inputs¶
| Source Parameter | File Type | File Format |
|---|---|---|
| Tracking File | experiment_annotations | csv |
| Zones File | movie_zones | csv |
Total Time in Zone¶
Total time is calculated by summing the number of frames.
Zone Area¶
Zone area is calculated the following way:
- Polygons (including rectangle): are calculated using the shoelace formula
- Ellipse: π * major axis * minor axis
Occupancy Score¶
Occupation score is a metric derived from the actual zone occupation / expected zone occupation. Specifically:
Number of frames spent in zone / Number of total frames * (Area of zone / Total area described by all zones)
Occupation scores greater than 1 represent occupation times greater than if the subject spent uniform time in every zone relative to its area.
Number of Zone Entries¶
The number of times the subject entered each zone.
Length of Zone Occupancy Events¶
Duration of continuous periods of zone occupancy.
Instantaneous Speed Calculation¶
Instantaneous speed is calculated from keypoint estimates by computing the Euclidean distance between consecutive centers of the bounding box and dividing by the time difference between consecutive frames. If the Pixels Per Cm parameter is specified, then the speed is converted from px/s to cm/s.
Outputs¶
Summary Table¶
The summary table is a .csv file which contains the results of the zone occupancy analysis. It contains the following columns:
- Zone Name
- Total Time Spent (s)
- Zone Area (Square Pixels)
- Occupancy Score
- Number of Entrances
- Average Duration (s)
Speed Table¶
The speed table is a .csv in the experiment annotations format and returns the instantaneous speed for each frame. It contains the following columns:
- Global Frame Number
- Frame Timestamp (s)
- Zone Name
- Speed
Events Table¶
The Events table is a .h5 in the event time stamps format and returns the timestamps of zone entries and exits.
Previews¶
The output annotations file will have the following previews which visualize the results.
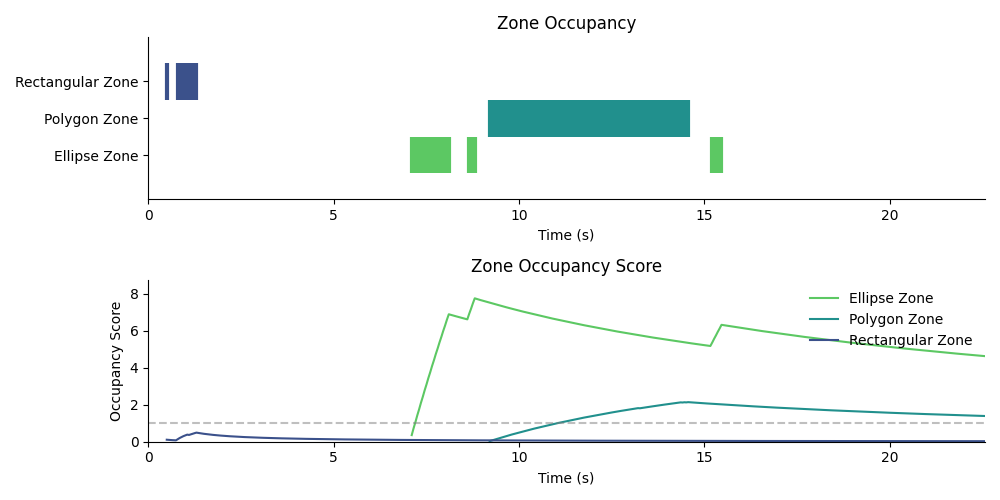
Zone Occupancy Overview:
Summary of subject zone occupancy. Top panel shows zone occupation as a function of time. Bottom panel shows occupancy score as a function of time.
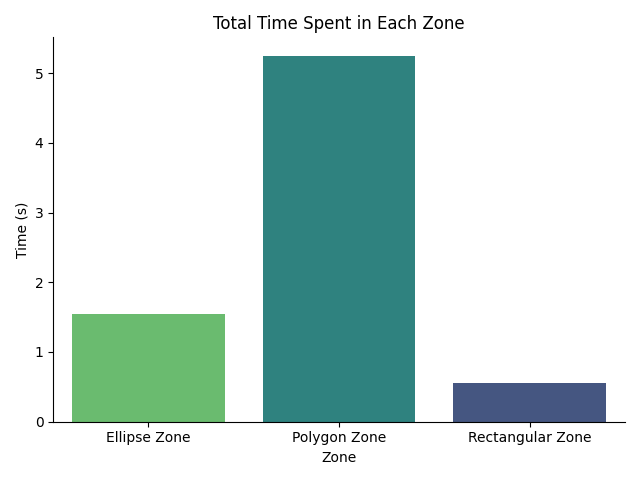
Total Time Spent in Each Zone:
The cumulative time (in seconds) the subject spent in each zone
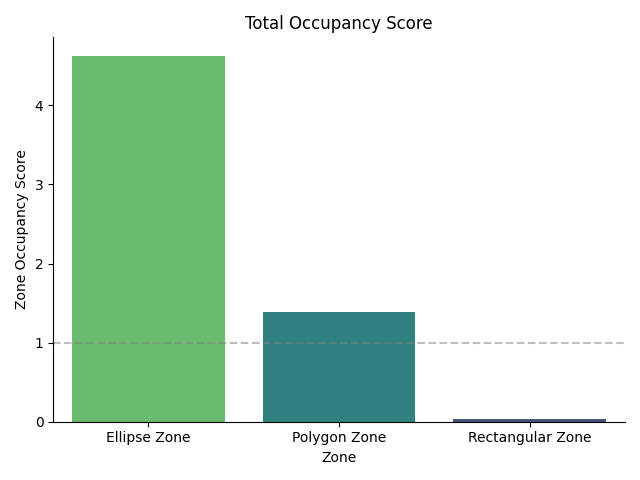
Total Occupancy Score:
The cumulative occupancy score across the entire session.
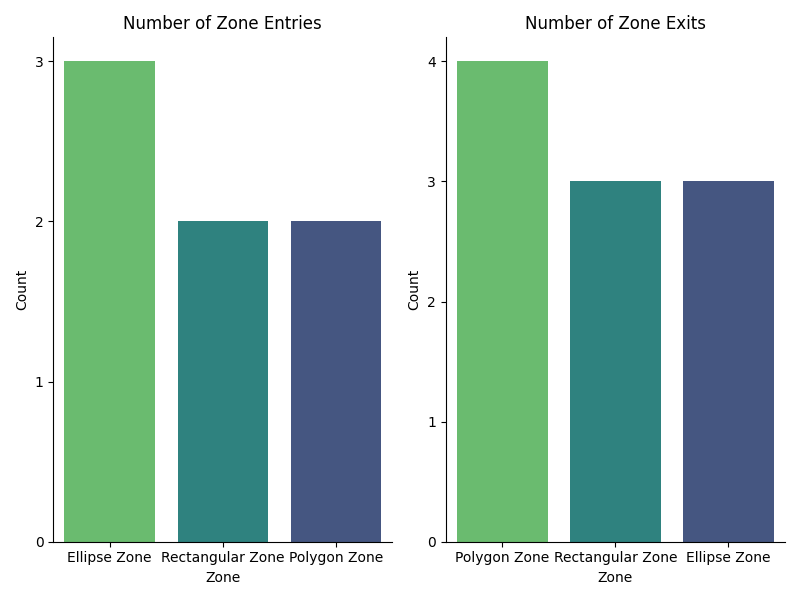
Number of Zone Entries:
Summary showing the number of times the subject entered each zone.
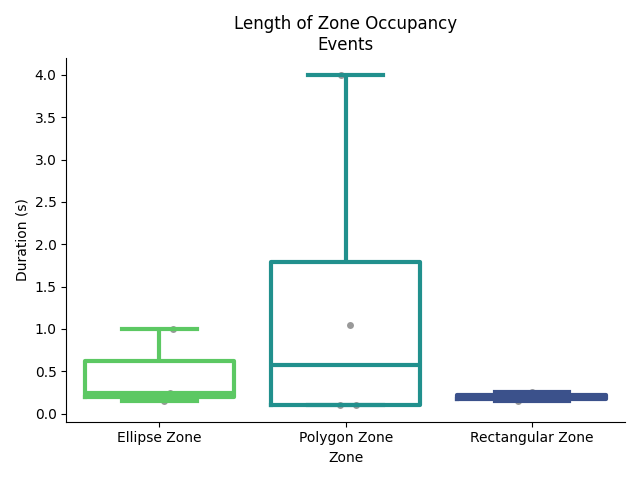
Length of Zone Occupancy Events:
Box plots with strip plot overlaid showing the distribution of durations the subject spent continuously in each zone. Each dot represents a single period.
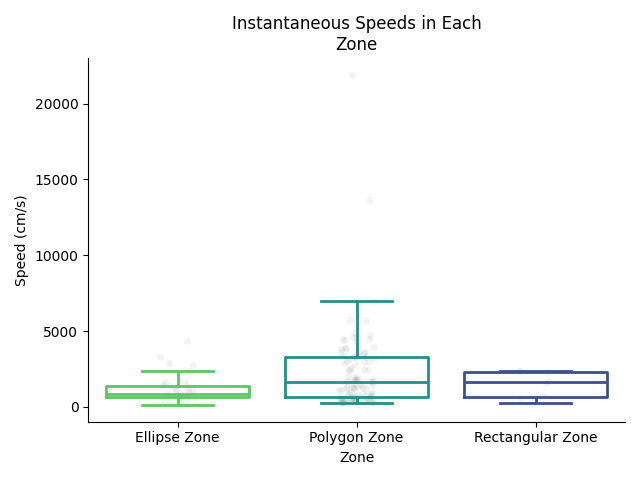
Instantaneous Speeds:
Box plots with strip plot overlaid showing the distributions of instantaneous speeds for each zone. Each dot represents an instantaneous speed computed from a single time point.
Next Steps¶
After running this tool, the outputs of this tool can be used as inputs to other tools.
The zone_events.h5 output can be used to compare neural activity surrounding zone events using:
The time_series_data.csv can be synchronized to a corresponding .isxd file using Map Annotations To ISXD Data, which can then be used as input to the following tools to observe differences in neural activity in different zones: